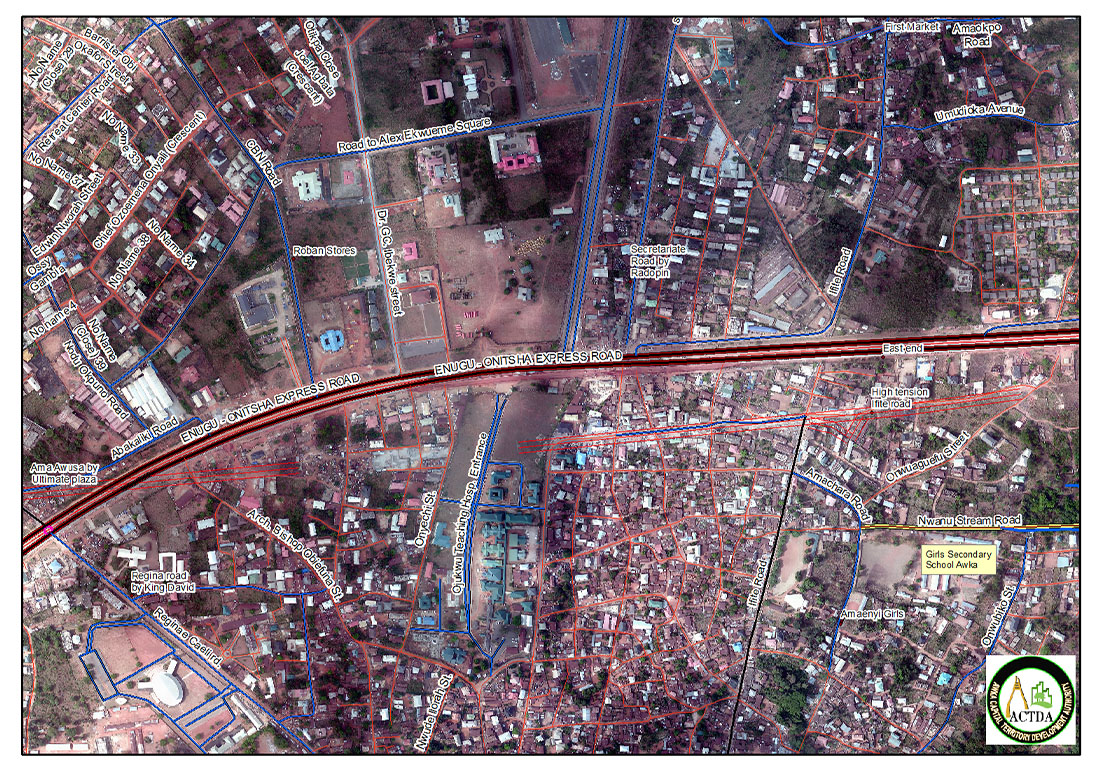
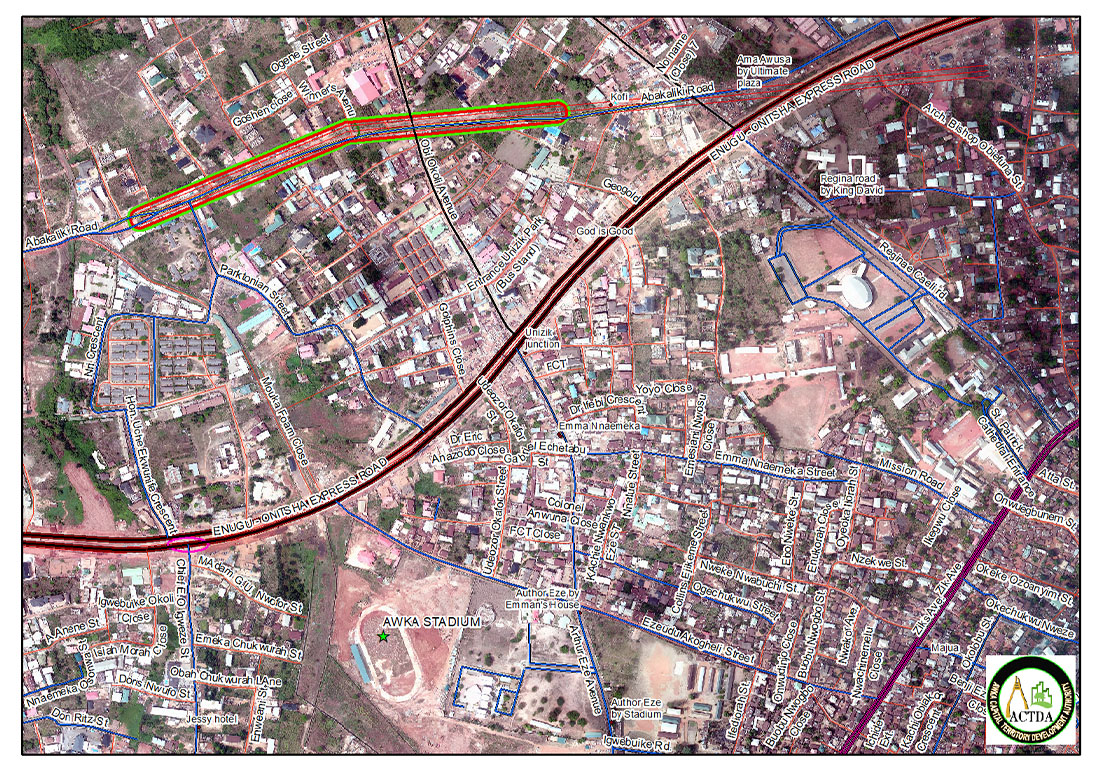
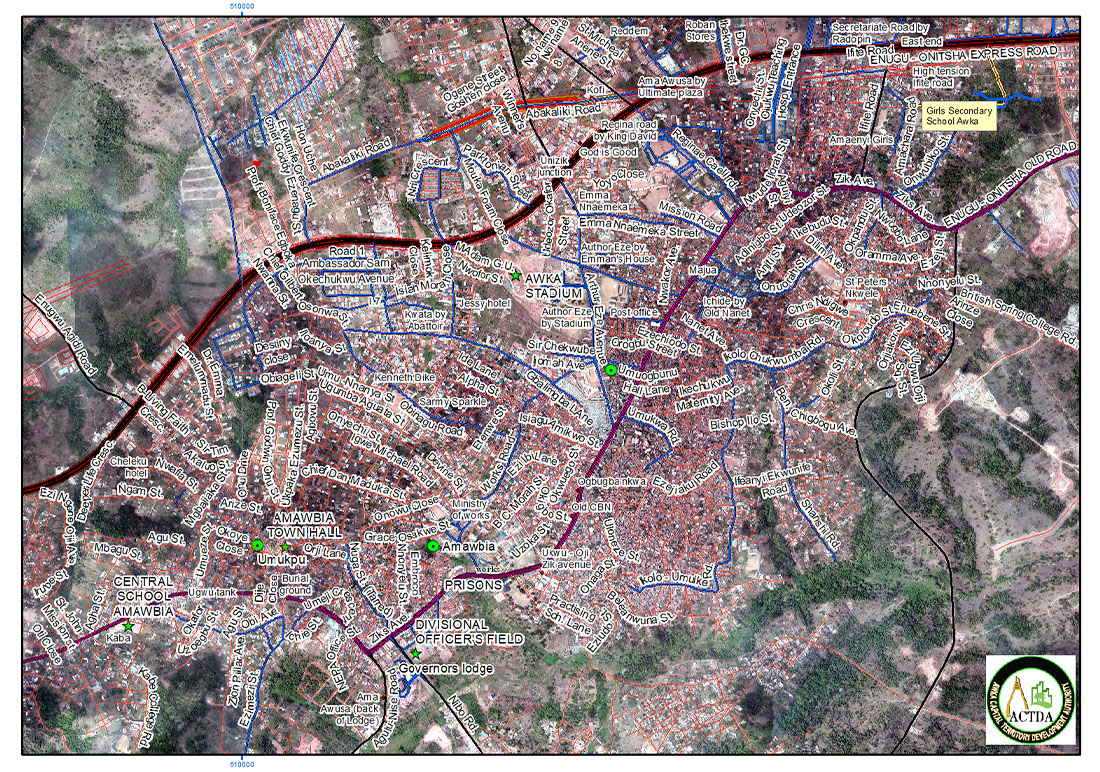
Growth Management Tools for City Planning and Development Control
Growth management tools are essential for city planning and development control agencies like ACTDA to ensure sustainable and organized urban development. These tools help manage the expansion of urban areas, prevent urban sprawl, and maintain the quality of life for residents.
1. Comprehensive Planning
A comprehensive plan is a fundamental tool that outlines the long-term vision for growth and development. It includes policies, goals, and guidelines that shape the future of the community. This plan serves as a blueprint for decision-making regarding land use, housing, transportation, infrastructure, and environmental protection.
2. Zoning Regulations
Zoning is a regulatory tool that divides a city into zones where certain land uses are permitted or prohibited. It helps implement the comprehensive plan by controlling the density and type of development, thus preventing incompatible land uses and preserving the character of neighborhoods.
3. Urban Growth Boundaries (UGBs)
UGBs define the limit to which a city can expand, protecting rural land and open spaces from development. This tool helps concentrate growth within the designated areas, encouraging denser development and efficient use of land and resources.
4. Adequate Public Facilities Ordinances (APFOs)
APFOs ensure that the necessary public facilities, such as schools, roads, and water systems, are in place to support new development. They prevent the overburdening of existing infrastructure and maintain service levels for the community.
5. Development Impact Fees
These fees are charged to developers to offset the costs of providing public services to new developments. Impact fees help fund infrastructure improvements and ensure that new growth pays its fair share of the costs.
6. Transfer of Development Rights (TDRs)
TDR programs allow landowners to sell development rights from their property to developers who want to increase the density of development in areas designated for growth. This tool helps preserve agricultural lands and open spaces while directing growth to more suitable areas.
7. Environmental Impact Assessments (EIAs)
EIAs evaluate the potential environmental impacts of proposed developments. They help decision-makers understand the environmental consequences and consider mitigation measures to reduce negative effects.
8. Public Participation
Engaging the community in the planning process is crucial. Public participation ensures that the voices of residents are heard and considered in the development of plans and policies.
9. Smart Growth Strategies
Smart growth promotes development that is environmentally sustainable, economically viable, and socially inclusive. It emphasizes mixed-use development, walkable neighborhoods, and transit-oriented development.
10. Geographic Information Systems (GIS)
GIS technology is used to analyze spatial data, map urban growth patterns, and support decision-making. It provides planners with a powerful tool to visualize and assess the impacts of growth.
By employing these growth management tools, ACTDA can effectively guide the development of the city, ensuring that it is well-planned, sustainable, and beneficial for current and future generations. For more detailed information on each tool and its application, refer to the comprehensive literature review and the case studies of various municipalities.